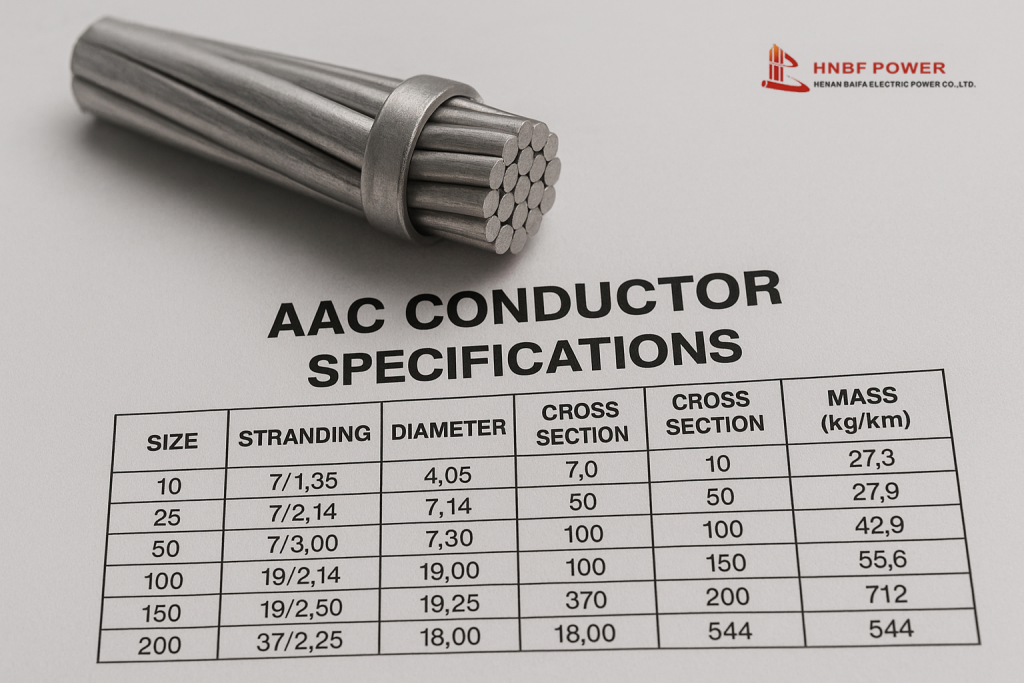
AAC Conductor Specifications play a vital role in defining the performance, safety, and reliability of modern electrical power networks. These conductors, made entirely of high-purity Aluminum 1350-H19, are widely used in overhead transmission and distribution lines due to their excellent conductivity, corrosion resistance, and lightweight structure. Designed according to international standards such as ASTM B231, IEC 61089, and BS 215, AAC conductors offer a dependable solution for short-span and medium-voltage power systems where efficiency and cost-effectiveness are critical.
By maintaining optimal ampacity, mechanical strength, and low resistance, AAC conductors continue to support power utilities and infrastructure developers in building reliable and scalable grids. Their versatility makes them suitable for urban distribution, rural electrification, and industrial power connections, particularly in areas where environmental durability and conductivity are priorities.
AAC Conductor Specifications Guide: Foundation of Modern Power Networks
In this guide, we will explain the structure, characteristics, applications, and key advantages of AAC conductor specifications that form the foundation of modern power networks.

AAC Conductor Specifications
AAC (All-Aluminum Conductor) is one of the most widely used types of overhead conductors in electrical transmission and distribution systems. Designed primarily for urban and short-distance power networks, AAC is made entirely of EC-grade aluminum (Aluminum 1350-H19), known for its excellent electrical conductivity and lightweight construction.
In compliance with ASTM B231 and IEC standards, AAC conductors are composed of concentrically stranded aluminum wires that provide strength and flexibility while maintaining low electrical resistance. These conductors are typically classified as Class AA for bare applications and Class A for covered ones, making them suitable for both low and medium voltage lines.
AAC conductors are valued for their high current-carrying capacity (ampacity), low cost, and easy installation, making them a preferred choice for short-span distribution networks and rural electrification projects.
Structure of AAC Conductor
The structure of an AAC conductor is concentric-lay stranded, meaning the aluminum wires are laid around a central wire in successive layers.
Key Structural Elements:
- Material: Aluminum 1350-H19 (EC Grade)
- Stranding: Typically 7, 19, 37, or more wires per conductor
- Configuration: Concentric layers around a single core wire
- Sizes: Available in both AWG and MCM sizes (e.g., 500 MCM, 1000 MCM)
Each strand contributes to the overall mechanical strength and electrical efficiency of the conductor. The uniform circular geometry reduces skin effect losses, ensuring consistent current flow.
The conductor’s design also makes it easy to splice, terminate, and install in various configurations, whether used in open-air installations or insulated systems.
Key Characteristics
AAC conductors are designed to balance conductivity, strength, and durability while remaining lightweight and cost-effective.
1. High Conductivity
AAC conductors offer approximately 61% IACS (International Annealed Copper Standard) conductivity, which allows them to efficiently carry electrical current over short to medium distances.
2. Corrosion Resistance
Being made entirely of aluminum, AAC conductors naturally resist atmospheric corrosion, especially in coastal and humid environments.
3. Flexibility and Ease of Handling
Their lightweight and flexible design makes installation quicker, reducing labor and equipment costs in large-scale power projects.
4. Standard Compliance
AAC conductors comply with global standards such as ASTM B231, BS 215, IS 398, and IEC 61089, ensuring consistent quality and interchangeability worldwide.
5. Mechanical Strength
Though AAC has lower tensile strength compared to ACSR (Aluminum Conductor Steel Reinforced), it is sufficient for short-span applications where mechanical load is moderate.
Applications of AAC Conductor
AAC conductors play a critical role in modern power transmission infrastructure.
Primary Applications:
- Urban Distribution Networks: Ideal for cities where short spans and high conductivity are required.
- Rural Electrification: Cost-effective solution for connecting remote communities.
- Low and Medium Voltage Lines: Used in networks up to 33 kV.
- Overhead Transmission Lines: In areas with low mechanical stress and shorter pole distances.
- Power Substations: For internal bus connections and interconnections between transformers and switchgear.
In marine or coastal areas, AAC’s corrosion resistance makes it a durable choice over steel-reinforced conductors.
Technical and Mechanical Properties
AAC conductors are defined by measurable parameters that determine their suitability for specific electrical and environmental conditions.
| Property | Typical Value | Standard Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Aluminum 1350-H19 | ASTM B231 / IEC 61089 |
| Conductivity | 61% IACS | ASTM B230 |
| Temperature Rating | Up to 75°C | IEC Standards |
| Tensile Strength | 90 – 200 MPa | ASTM Specifications |
| DC Resistance (20°C) | 0.164–0.641 Ω/km (varies by size) | ASTM B231 |
| Weight per km | 50 – 800 kg/km (depending on strand count) | Standard Table |
| Ampacity | Up to 900 Amps (size-dependent) | Manufacturer Data |
| Typical Stranding | 7, 19, 37, 61 wires | Industry Standard |
These specifications ensure AAC conductors meet performance requirements for voltage stability, current flow, and safe mechanical operation in diverse environmental conditions.
Comparison with Other Conductors
When selecting conductors for power networks, engineers often compare AAC with other types like AAAC (All Aluminum Alloy Conductor) and ACSR (Aluminum Conductor Steel Reinforced).
| Parameter | AAC | AAAC | ACSR |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material | Pure Aluminum (1350-H19) | Aluminum Alloy | Aluminum + Steel Core |
| Conductivity | 61% IACS | 52.5% IACS | 59.5% IACS |
| Strength | Moderate | High | Very High |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Excellent | Moderate |
| Weight | Light | Medium | Heavy |
| Cost | Low | Medium | Medium–High |
| Best Use | Short spans, cities, coastal areas | Medium spans, long distances | Long spans, heavy load areas |
AAC stands out for its high conductivity and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for urban distribution and short-distance overhead lines, while ACSR dominates long-span transmission due to higher tensile strength.
Advantages of AAC Conductors
AAC conductors offer numerous operational and economic advantages for utilities and contractors.
- High Electrical Efficiency – The low resistance ensures minimal line losses.
- Corrosion Resistance – 100% aluminum design prevents oxidation and rust.
- Lightweight – Easier handling, installation, and reduced tower loading.
- Cost-Effective – Lower material and installation costs compared to ACSR.
- Compatibility – Meets multiple international standards (ASTM, IEC, BS).
- Sustainability – Aluminum is recyclable and environmentally friendly.
- Easy Maintenance – Simplified inspection and repair process.
For networks prioritizing conductivity and economy, AAC is one of the most efficient conductor choices available today.
Limitations of AAC Conductors
While AAC conductors perform exceptionally well in specific applications, they have certain limitations:
- Lower Tensile Strength: Unsuitable for long spans or heavy load areas.
- Higher Sag: Requires closer pole spacing compared to ACSR or AAAC.
- Limited Mechanical Endurance: May deform under extreme wind or ice load.
- Shorter Application Range: Best for low and medium voltage networks, not for high-voltage transmission lines.
Despite these, AAC remains a practical choice for cost-driven projects with predictable environmental conditions.
Where to Buy AAC Conductors
For reliable AAC conductors that meet ASTM B231, BS 215, and IEC 61089 standards, HNBFpower is a trusted global manufacturer and supplier.
Why Choose HNBFpower:
- In-house testing and quality assurance under ISO and ASTM compliance
- Wide range of AAC, AAAC, and ACSR conductors available in multiple sizes
- Custom manufacturing and packaging solutions for OEMs and utilities
- Global supply network ensuring on-time delivery and competitive pricing
HNBFpower’s AAC conductors are used in urban distribution, rural electrification, and industrial power systems worldwide.
- What is an AAC conductor?
An AAC (All Aluminum Conductor) is an electrical cable made entirely from strands of high-purity aluminum. It is mainly used for overhead power transmission and distribution because it is lightweight, conducts electricity well, and is cost-effective. - Which international standards do AAC conductors follow?
AAC conductors are manufactured according to standards like ASTM B231 (USA), BS 215 (UK), and IEC 61089 (International). These standards specify the correct materials, construction, diameter, resistance, and tensile strength needed for safe and reliable performance. - What material is used to make an AAC conductor?
AAC conductors are made from Aluminum 1350-H19, which is a very pure electrical-grade aluminum. This specific grade provides excellent electrical conductivity (about 61% IACS) and natural resistance to rust and corrosion. - What are the main advantages of AAC conductors, and where are they used?
AAC conductors offer high electrical conductivity, are lightweight, and resist corrosion very well. They are best used for short-span power lines in cities, towns, substations, and industrial sites where high strength is not required. - What is the difference between AAC and ACSR conductors, and when should each be used?
AAC conductors are made only of aluminum, making them highly conductive but less strong. ACSR (Aluminum Conductor Steel Reinforced) includes a core of steel wires, giving it extra strength for long spans and areas with strong winds or heavy mechanical loads. AAC is ideal for short distances where only good conductivity and corrosion resistance are needed, while ACSR is preferred for long spans with more mechanical stress.
AAC conductors remain a cornerstone in modern power transmission systems, especially for urban and short-distance electrical networks. Built with high-conductivity aluminum strands, they provide a combination of lightweight design, corrosion resistance, and electrical efficiency.
While not suitable for long-span or high-tension applications, AAC continues to deliver value where cost, conductivity, and installation speed matter most.
Manufacturers like HNBFpower ensure consistent quality through adherence to ASTM, IEC, and BS standards, offering reliable solutions for today’s evolving power infrastructure.

